Obesity in Indoor Dogs:
Introduction:
Obesity in dogs is a growing concern, especially for indoor dogs that may not get as much exercise as their outdoor counterparts. The condition can lead to various health issues and significantly reduce the quality of life of your furry friend. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, and treatment of obesity in indoor dogs. We will also discuss preventive measures to ensure your dog stays healthy and fit.

Understanding Obesity in Dogs

What is Obesity?
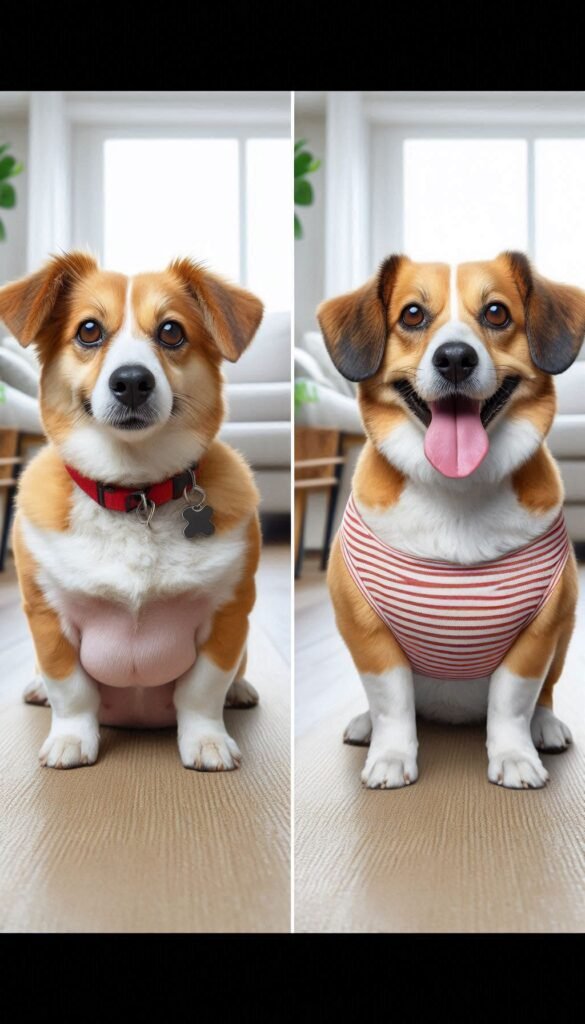
Obesity in dogs is defined as an excessive accumulation of body fat, usually resulting from a caloric imbalance where energy intake exceeds energy expenditure. A dog is considered obese if its body weight exceeds the ideal weight for its breed and age by more than 20%.
The Ultimate Solution to Your Dog Care Problems

Causes of Obesity in Indoor Dogs
01-Overfeeding:
One of the primary causes of obesity in indoor dogs is overfeeding. This includes giving too much food during meals, offering high-calorie treats, and feeding table scraps.
02-Lack of Exercise:
Indoor dogs often do not get enough physical activity. Limited space and a sedentary lifestyle contribute to weight gain.
03-Poor Diet:
Feeding dogs low-quality food that is high in fat and carbohydrates can lead to weight gain. A balanced diet is essential for maintaining a healthy weight.
04-Genetic Factors:
Certain breeds are more prone to obesity due to their genetic makeup. Breeds like Labradors, Beagles, and Dachshunds are particularly susceptible.
05-Medical Conditions:
Health issues such as hypothyroidism, Cushing’s disease, and insulinoma can contribute to weight gain in dogs.
06-Age:
As dogs age, their metabolism slows down, making them more prone to weight gain if their diet and exercise levels are not adjusted accordingly.
07-Spaying/Neutering:
Hormonal changes following spaying or neutering can lead to a reduced metabolic rate and increased appetite, contributing to weight gain
Symptoms of Obesity in Dogs
01-Excessive Weight Gain:
The most obvious sign is a noticeable increase in body weight.
02-Difficulty Breathing:
Overweight dogs often have trouble breathing, especially during physical activity.
03-Reduced Stamina:
Obese dogs may tire easily and show reluctance to exercise.
04-Joint Problems:
Excess weight puts additional strain on joints, leading to arthritis and other joint issues.
05-Inability to Feel Ribs:
In a healthy dog, you should be able to feel the ribs without pressing hard. In obese dogs, a thick layer of fat covers the ribs.
06-Behavioral Changes:
Obesity can lead to lethargy, depression, and a lack of interest in activities the dog once enjoyed.
The Natural Formula That
Supports Your Dog’s Health
Pawbiotix is the only nutritional formula designed to help your dog achieve optimal and balanced levels of all five healthy gut bacteria they need to thrive.
Health Risks Associated with Obesity
01-Diabetes Mellitus:
Obesity is a significant risk factor for diabetes, as excess fat can interfere with insulin production and regulation.
02-Heart Disease:
Excess weight puts strain on the heart, leading to cardiovascular problems.
03-Respiratory Issues:
Obese dogs often suffer from respiratory problems due to the extra weight on their chest.
04-Joint and Mobility Problems:
The added weight can cause or exacerbate joint problems like arthritis, hip dysplasia, and intervertebral disc disease.
05-High Blood Pressure:
Obesity can lead to hypertension, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
06-Decreased Lifespan:
Obese dogs generally have a shorter lifespan compared to their healthy-weight counterparts.
07-Liver Disease:
Excess fat can accumulate in the liver, leading to hepatic lipidosis.
Treatment for Obesity in Indoor Dogs
01-Dietary Changes
- Portion Control: Measure your dog’s food and feed them the recommended amount for their ideal weight, not their current weight.
- High-Quality Diet: Switch to a high-quality, low-calorie dog food that is rich in protein and fiber.
- Eliminate Table Scraps: Avoid feeding your dog human food, which is often high in fat and calories.
- Healthy Treats: Offer low-calorie treats or use vegetables like carrots and green beans as treats.
02-Exercise Routine
- Daily Walks: Ensure your dog gets at least 30 minutes of walking daily. Gradually increase the duration and intensity as your dog’s stamina improves.
- Interactive Play: Engage your dog in play sessions with toys like balls, frisbees, and tug ropes.
- Indoor Activities: Create an indoor obstacle course or use interactive toys to keep your dog active indoors.
- Dog Parks: Visit dog parks where your dog can run and socialize with other dogs.
03-Regular Vet Check-Ups
- Health Monitoring: Regular vet visits are essential to monitor your dog’s weight and overall health.
- Customized Weight Loss Plan: Your vet can create a personalized weight loss plan tailored to your dog’s needs.
- Medical Interventions: In some cases, medication or supplements may be prescribed to help with weight loss.
04-Behavioral Modifications
- Scheduled Feeding: Establish regular feeding times instead of free-feeding.
- Positive Reinforcement: Use praise and healthy treats to reward good behavior and adherence to the new diet and exercise routine.
- Avoid Emotional Feeding: Do not use food as a way to comfort or entertain your dog.
05-Weight Management Programs
- Professional Help: Consider enrolling your dog in a weight management program supervised by veterinary professionals.
- Support Groups: Join online forums or local groups for tips, support, and motivation from other dog owners dealing with similar issues.

Preventing Obesity in Indoor Dogs
Prevention is always better than cure. Here are some tips to prevent obesity in indoor dogs:
- Balanced Diet: Feed your dog a balanced diet with appropriate portions for their age, breed, and activity level.
- Regular Exercise: Ensure your dog gets regular physical activity to burn off excess calories.
- Healthy Treats: Offer healthy, low-calorie treats in moderation.
- Monitor Weight: Regularly check your dog’s weight and adjust their diet and exercise routine as needed.
- Spaying/Neutering Considerations: If your dog is spayed or neutered, be mindful of their calorie intake and exercise needs.
- Avoid Overfeeding: Do not give in to begging or feed your dog table scraps.
- Regular Vet Check-Ups: Schedule regular vet visits to monitor your dog’s weight and overall health.

Case Study: Successful Weight Loss in an Obese Dog
Case Study: Bella’s Journey to a Healthy Weight
Bella, a 5-year-old Labrador Retriever, weighed 90 pounds, significantly more than the ideal weight for her breed. Her owner, Sarah, noticed Bella had become lethargic and struggled to keep up during walks. Concerned, Sarah took Bella to the vet, who diagnosed her with obesity and developed a comprehensive weight loss plan.
Initial Assessment:
- Weight: 90 pounds
- Body Condition Score: 8/9 (Obese)
- Health Issues: Early signs of arthritis, difficulty breathing, and low energy levels.
Treatment Plan:
- Dietary Changes: The vet recommended a high-quality, low-calorie dog food and instructed Sarah to feed Bella the recommended portion for her target weight of 70 pounds.
- Exercise Routine: Bella started with 15-minute walks twice a day, gradually increasing to 30 minutes as her stamina improved.
- Healthy Treats: Sarah switched to low-calorie treats and used vegetables like carrots and cucumbers as rewards.
- Regular Vet Check-Ups: Monthly vet visits were scheduled to monitor Bella’s progress and make necessary adjustments to her diet and exercise routine.
Results:
- Weight Loss: Bella lost 20 pounds over six months, reaching her target weight of 70 pounds.
- Improved Health: Her energy levels increased, and the early signs of arthritis were managed more effectively.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Bella became more active, enjoying longer walks and playtime with Sarah.
Conclusion:
Obesity in indoor dogs is a serious health issue that requires prompt attention and proactive management. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, you can help your dog achieve and maintain a healthy weight. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and routine vet check-ups are crucial in preventing and managing obesity. Remember, a healthy dog is a happy dog, and taking these steps will ensure your furry friend enjoys a long, active, and fulfilling life.
By following the guidelines outlined in this article, you can effectively manage your indoor dog’s weight and improve their overall well-being. Whether it’s through dietary changes, increased physical activity, or regular health monitoring, your commitment to your dog’s health will pay off in the form of a happier, healthier companion.


. What are the main causes of obesity in indoor dogs?
Answer: Obesity in indoor dogs is primarily caused by a combination of factors including overfeeding, lack of exercise, high-calorie diets, and genetic predisposition. Indoor dogs often have less opportunity to exercise compared to outdoor dogs, leading to weight gain if their calorie intake is not adjusted accordingly.
How can I tell if my dog is overweight?
Answer: You can tell if your dog is overweight by observing their body shape and checking their ribs. A healthy dog should have a noticeable waistline and you should be able to feel their ribs without pressing too hard. If these features are not evident, your dog might be overweight. Regular weigh-ins and consultations with your veterinarian can provide more accurate assessments.
What health problems are associated with obesity in dogs?
Answer: Obesity in dogs can lead to a range of health problems including diabetes, heart disease, arthritis, respiratory issues, and decreased lifespan. Overweight dogs are also more prone to developing joint and mobility problems due to the extra weight their bodies have to carry.
What are some effective ways to help my dog lose weight?
Answer: Effective ways to help your dog lose weight include:Diet: Switch to a high-quality, low-calorie dog food and measure portions carefully.
Exercise: Increase your dog’s physical activity with regular walks, playtime, and interactive toys.
Treats: Limit treats and choose healthy, low-calorie options.
Consistency: Maintain a regular feeding and exercise schedule.
Veterinary Support: Work with your veterinarian to create a tailored weight loss plan and monitor your dog’s progress.
How often should I take my overweight dog to the vet?
Answer: If your dog is overweight, it is advisable to visit the vet more frequently than for routine check-ups. Initially, you might need to visit the vet every month to monitor weight loss and adjust the treatment plan as needed. Once your dog reaches a healthier weight, regular biannual check-ups can help maintain their health and prevent future weight gain.
The Importance of Regular Dental Check-ups: Preventing Major Oral Health Issues
Caring for the health of teeth is very crucial to one’s health of the body….
Is Social Media Bad for Mental Health?
Is Social Media Bad for Mental Health? Exploring the Impact on Well-Being Social media has…
Probiotics Specially Designed for the Health of Your Teeth and Gums
Brand New Probiotics Specially Designed For TheHealth Of Your Teeth And Gums Try ProDentim: a unique…
The Health Benefits of Daily Coffee Consumption: Boost Your Focus, Mood, and More
Introduction: Coffee can be described as one of the most popular beverages in the globe,…
Top 5 Amazon Coffee Makers for Perfect Brews: Discover Your Ideal Coffee Machine
offee occupies an important place in many people’s lives, it is not only drink which…
Top 5 Best Coffee Shops in New York for a Perfect Coffee Date
When it comes to choosing the perfect coffee shop for a romantic coffee date in…
-
Brown Wooden Cat House | Dog House
Original price was: ₨ 16,499.₨ 11,999Current price is: ₨ 11,999. -
Candy Jar | Handmade Wooden Candy Jar | Pakistani Handicraft Nakashi Candy Jar
Original price was: ₨ 4,449.₨ 3,999Current price is: ₨ 3,999. -
Cat House | Brti Cat House | Indoor Puppy House | Pet House
Original price was: ₨ 30,000.₨ 28,499Current price is: ₨ 28,499.














