Understanding and Managing Parasites in Dogs: A Comprehensive Guide to Common Diseases in Dogs
Introduction
Parasites are a significant concern for dog owners and a prevalent issue among common diseases in dogs. These unwelcome guests can cause a range of health problems, from mild discomfort to severe illness. Understanding the types of parasites, their symptoms, and how to treat and prevent them is crucial for maintaining your dog’s health and well-being.

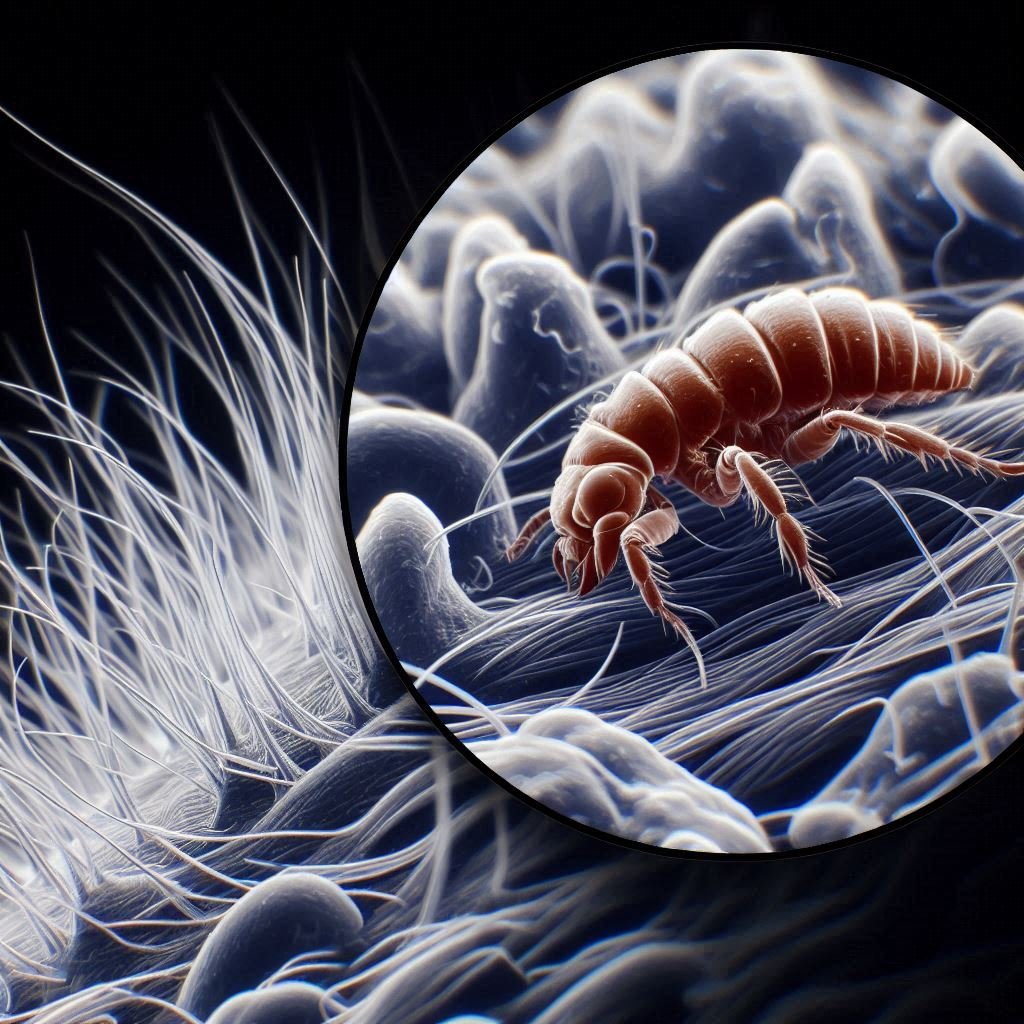
Types of Parasites in Dogs
External Parasites
01-Fleas
- Description: Small, wingless insects that feed on your dog’s blood.
- Symptoms: Itching, redness, and flea dirt on the dog’s skin.
- Treatment: Topical treatments, oral medications, and regular grooming.
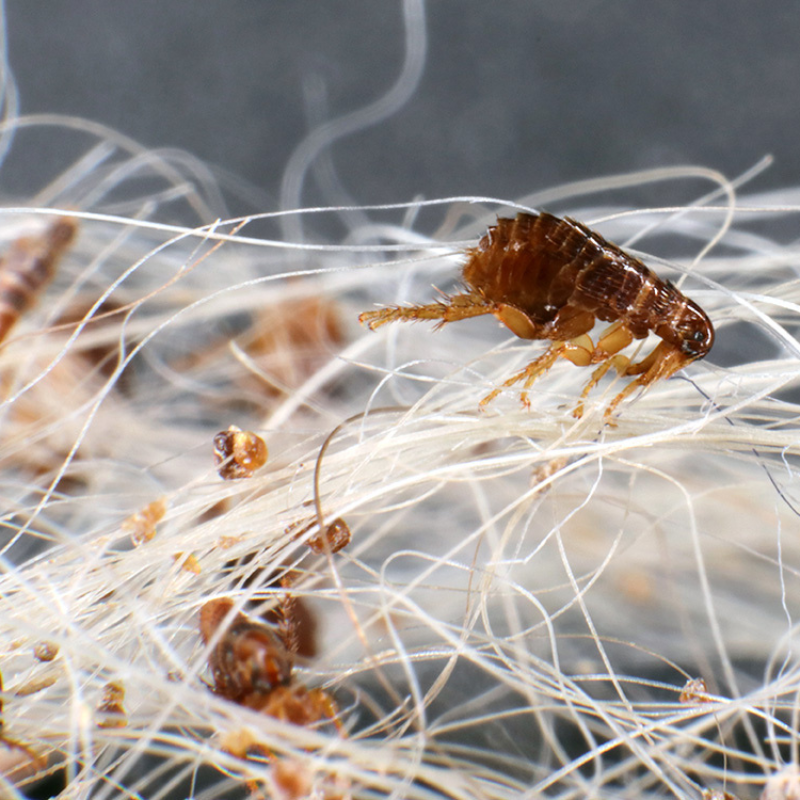

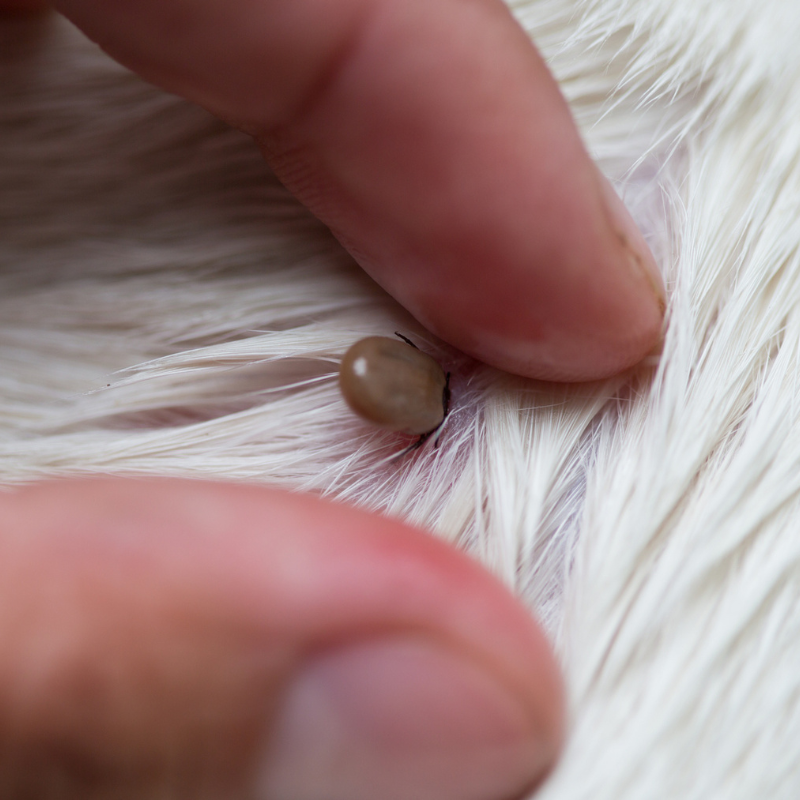
02-Ticks
- Description: Arachnids that attach to the dog’s skin and feed on blood.
- Symptoms: Visible ticks on the skin, localized redness, and irritation.
- Treatment: Tick removal tools, topical treatments, and preventive collars.
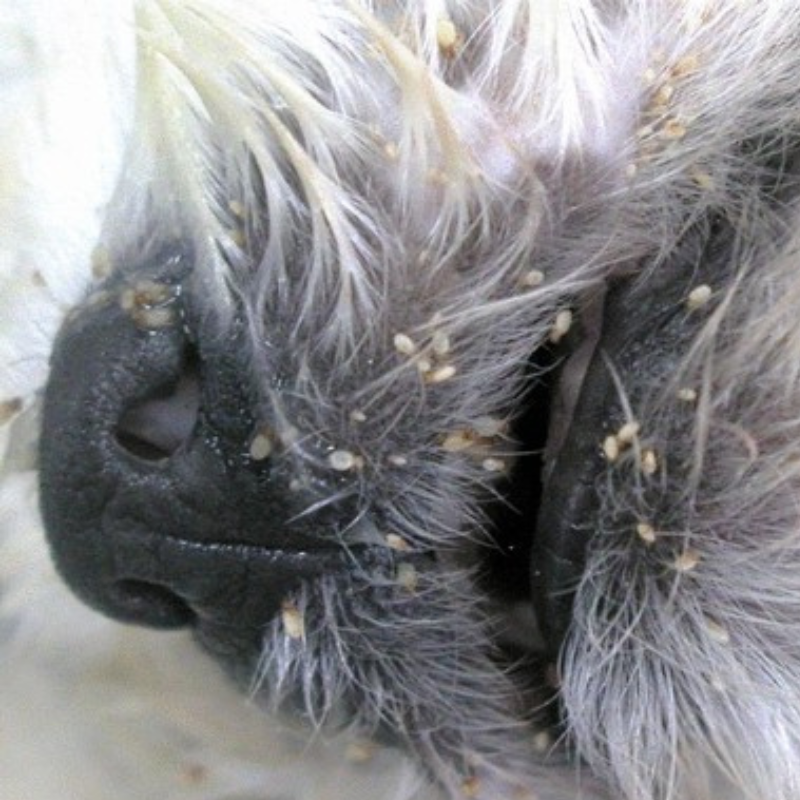
03-Mites
- Description: Tiny parasites causing conditions like mange.
- Symptoms: Hair loss, itching, and skin inflammation.
- Treatment: Medicated baths, topical treatments, and sometimes oral medications.

04-Lice
- Description: Wingless insects living on the dog’s skin and hair.
- Symptoms: Itching, hair loss, and visible lice or nits.
- Treatment: Insecticidal shampoos and grooming.
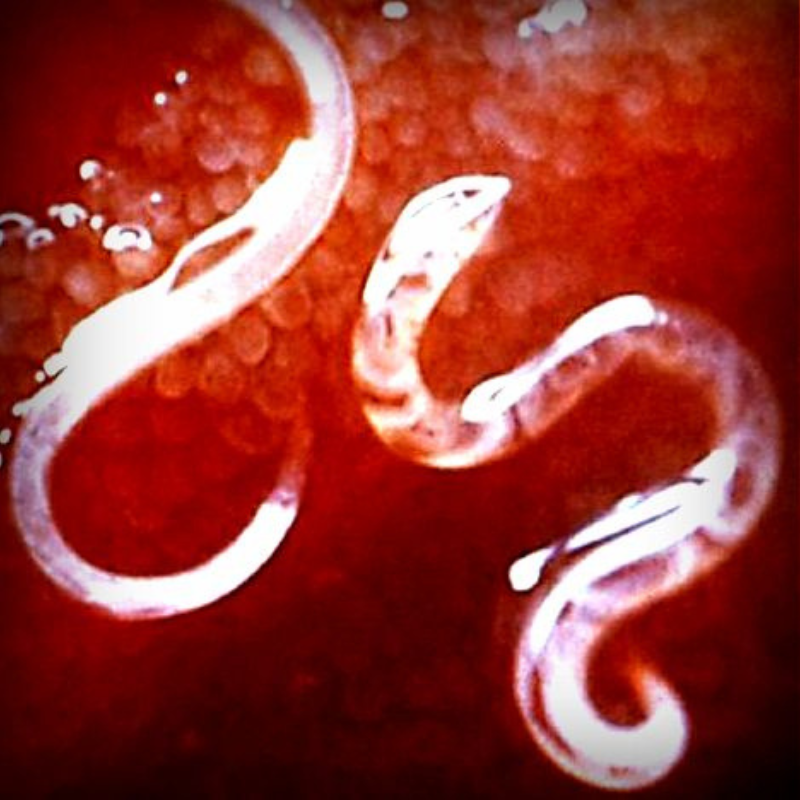
Internal Parasites
01-Roundworms
- Description: Worms that live in the intestines.
- Symptoms:Weight loss, pot-bellied appearance, vomiting, and diarrhea.
- Treatment: Deworming medications and maintaining hygiene.

02-Hookworms
- Description:Worms that attach to the intestinal wall.
- Symptoms: Anemia, weight loss, and bloody stools.
- Treatment:Deworming medications and ensuring a clean environment.
03-Tapeworms
- Description: Long, flat worms that attach to the intestines.
- Symptoms: Scooting, weight loss, and segments of worms in the feces.
- Treatment: Deworming medications and flea control.

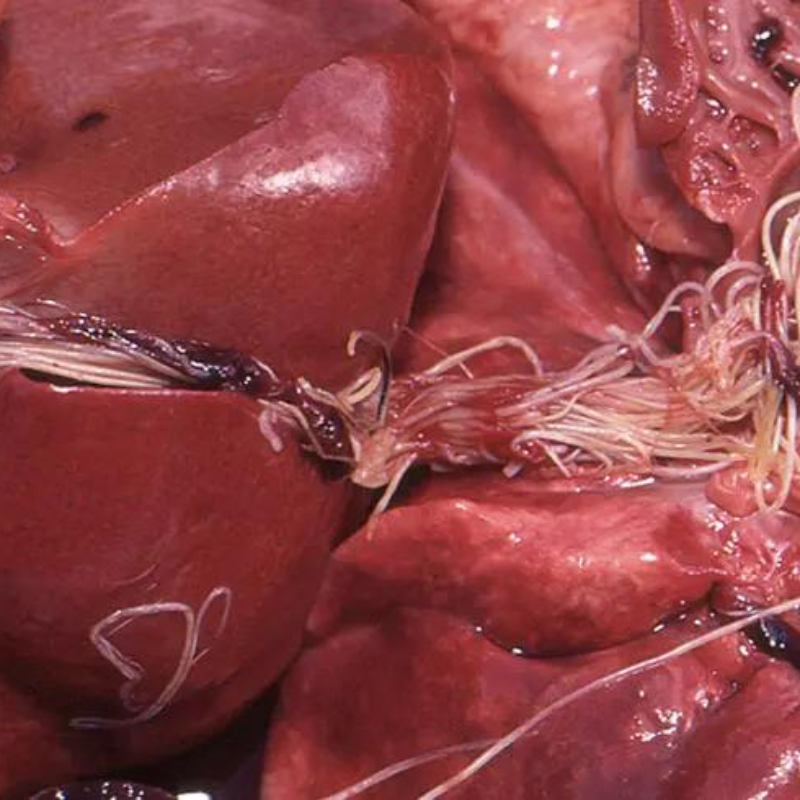
04-Heartworms
- Description: Worms that live in the heart and blood vessels.
- Symptoms: Coughing, fatigue, weight loss, and heart failure.
- Treatment: Injectable medications and preventive heartworm treatments.

Symptoms of Parasitic Infections
Parasitic infections can manifest in various ways, depending on the type of parasite. Common symptoms include:
- Itching and scratching
- Hair loss
- Skin redness and irritation
- Visible parasites on the skin or in the feces
- Weight loss and poor coat condition
- Gastrointestinal issues like vomiting and diarrhea
- Lethargy and weakness
Diagnosis and Tests
Diagnosing parasitic infections typically involves:
- Physical Examination: Checking the dog’s coat, skin, and overall health.
- Fecal Tests: Analyzing stool samples for the presence of eggs or parasites.
- Blood Tests: Detecting blood-borne parasites like heartworms.
- Skin Scrapes: Identifying skin parasites like mites.
Treatment Options
- Topical Treatments: Medications applied directly to the skin to kill external parasites.
- Oral Medications: Pills or chewables that treat internal and some external parasites.
- Injections: Used primarily for heartworm treatment and prevention.
- Medicated Baths: Shampoos and dips that eliminate external parasites.
- Environmental Control: Cleaning the dog’s living area to remove parasites and prevent re-infestation.


Preventive Measures
Preventing parasitic infections is vital for your dog’s health. Effective strategies include:
- Regular Vet Check-ups: Routine examinations to detect early signs of parasites.
- Preventive Medications: Monthly treatments for fleas, ticks, and heartworms.
- Grooming and Hygiene: Regular baths and grooming to keep parasites at bay.
- Clean Living Environment: Keeping your home and yard clean to minimize exposure to parasites.
- Diet and Nutrition: Providing a balanced diet to strengthen the immune system.
Case Studies
Consider the story of Max, a Labrador Retriever, who suffered from a severe flea infestation. Max’s owner, Sarah, noticed him scratching incessantly and losing fur. A visit to the vet confirmed a flea problem. After a thorough treatment plan involving topical medications, flea baths, and home cleaning, Max recovered and is now flea-free. Sarah now uses monthly preventive treatments to keep Max healthy.
Expert Insights
Dr. Emily Johnson, a veterinary parasitologist, emphasizes the importance of year-round parasite prevention. “Parasites are not just a seasonal problem; they can affect your dog anytime. Regular preventive treatments and veterinary check-ups are essential to keep your pet safe,” she advises.
Conclusion
Parasites are a common disease in dogs, but with the right knowledge and preventive measures, you can protect your furry friend from these harmful invaders. Regular veterinary care, preventive treatments, and maintaining a clean environment are key to ensuring your dog’s health and happiness.
What are the most common parasites in dogs?
The most common parasites include fleas, ticks, mites, lice, roundworms, hookworms, tapeworms, and heartworms.
How can I tell if my dog has parasites?
Symptoms vary but may include itching, hair loss, weight loss, gastrointestinal issues, and visible parasites in the stool or on the skin.
What is the best way to prevent parasitic infections in dogs?
Regular vet check-ups, monthly preventive treatments, grooming, and maintaining a clean living environment are effective preventive measures.
Can parasites in dogs be transmitted to humans?
Yes, some parasites, like roundworms and hookworms, can be transmitted to humans, making it crucial to practice good hygiene and preventive care.
How often should I deworm my dog?
It’s recommended to deworm puppies every 2-3 weeks until 12 weeks old and then monthly until 6 months. Adult dogs should be dewormed at least every three months.
The Importance of Regular Dental Check-ups: Preventing Major Oral Health Issues
Caring for the health of teeth is very crucial to one’s health of the body….
Is Social Media Bad for Mental Health?
Is Social Media Bad for Mental Health? Exploring the Impact on Well-Being Social media has…
Probiotics Specially Designed for the Health of Your Teeth and Gums
Brand New Probiotics Specially Designed For TheHealth Of Your Teeth And Gums Try ProDentim: a unique…
The Health Benefits of Daily Coffee Consumption: Boost Your Focus, Mood, and More
Introduction: Coffee can be described as one of the most popular beverages in the globe,…
Top 5 Amazon Coffee Makers for Perfect Brews: Discover Your Ideal Coffee Machine
offee occupies an important place in many people’s lives, it is not only drink which…
Top 5 Best Coffee Shops in New York for a Perfect Coffee Date
When it comes to choosing the perfect coffee shop for a romantic coffee date in…
-
Brown Wooden Cat House | Dog House
Original price was: ₨ 16,499.₨ 11,999Current price is: ₨ 11,999. -
Candy Jar | Handmade Wooden Candy Jar | Pakistani Handicraft Nakashi Candy Jar
Original price was: ₨ 4,449.₨ 3,999Current price is: ₨ 3,999. -
Cat House | Brti Cat House | Indoor Puppy House | Pet House
Original price was: ₨ 30,000.₨ 28,499Current price is: ₨ 28,499.












